The Sun – Origination, Life and Death
The Sun has always evoked curiosity, fear, fascination and admiration in Man from time immemorial. The Sun is just one among millions of the stars in the universe. It is neither the biggest nor the smallest star. But, without the Sun life is impossible in the earth and hence the Sun is the real superstar for the living beings.
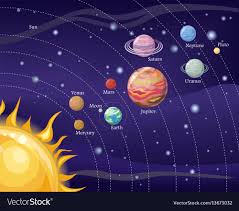
The solar system
The solar system includes the Sun and other objects that orbit it. The solar system consists of eight planets, their moons and smaller objects like comets, asteroids and meteoroids. These objects are held in their position by the powerful pull caused by an invisible force called gravity emanating from the Sun. The four planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are fairly small rocky bodies and closer to the Sun. Then there is a belt of smaller rocks named asteroids moving around the star. The remaining four planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are giants, composed mostly of gas and farther away from the belt of asteroids. All the eight planets orbits around the star in roughly circular orbits.
Why is the Sun important?
Life on the Earth survives because of the light and heat originating from the Sun. Constant warming rays of the star keeps our planet habitable. All celestial bodies that revolve around the star is held in their orbit by the force gravity. The invisible bubble called heliosphere created by the Sun protects the planets from cosmic radiations.
What constitute the Sun? What are the features of the Sun?
Though the Sun looks just a little bigger than the Moon while watching from the earth, the fact is that the star itself contains 99.86 percent of the entire mass of the solar system. The size of the Sun is around 3,30,000 bigger than the Earth and a thousand times massive than Jupiter, the largest planet of the solar system. The star has a diameter of 13,92,000 Km and the surface area is 11,900 times that of the Earth. The average distance between the Sun and the Earth is 149.6 million Km. The second nearest star to our planet, Proxima Centauri, is 2,70,000 times farther than the Sun. The light from the Sun takes eight minutes and twenty seconds to reach the earth whereas the time required for the light from Proxima Centauri is four years. Because of this huge distance, other stars look very small. The distance between the Sun and the Earth is 391 times that of the distance between the Moon and the Earth.
The sun is an almost perfect sphere, but is not solid. It is a ball of burning gases composed of 74.9 per cent Hydrogen, 23.8 per cent Helium and 2 per cent other gases. The core of the star is filled with hydrogen gas. Hydrogen gets converted into helium when it undergoes immense heat and pressure through a process called nuclear fusion. Light and heat of the Sun is created from this immense energy generating process. The Sun has different layers with varying temperatures. The different layers of the Sun are corona, radiative zone, tachocline, convective zone, photosphere and atmosphere.
The surface of the Sun has 5505 degree Celsius. The temperature of the core of the star is estimated to be in the range of 15 million degrees Celsius. The destructive heat at the core of the Sun becomes creative and essential by the time it reaches the surface of the Earth by covering a distance of approximately 150 million Km. The Sun is 4,00,000 times brighter than the full Moon. The sight of the Moon is appealing as it is less brighter and because the light from the Moon is the light from the Sun reflected. A measure called ‘Magnitude’ first conceived by Hipparchus is used to measure brightness of objectives and based on this scale, the Sun has a magnitude of -26.74
Origination of the Sun and planets
According to scientists, celestial bodies are not eternal and they too have a point of origination, growing old and death through disintegration. But the cycle is much longer compared to human being. It is believed that the solar system formed around 4.6 billion years back from a giant, rotating cloud of gas and dust known as the solar nebula. As the nebula collapsed due to its gravity, it spun faster and took the shape of disk. The Sun formed when the gravitational pull, attracted most of the material to the centre, forming a huge dusty cloud. The young star was initially a ball of hydrogen and helium. Over tens of millions of years, the temperature and pressure inside increased causing fusion of hydrogen, the present driving force of the star. Planets were formed from the remaining material. They too were hot initially but cooled off over a period of time as they were small and thus became planets of today.
Dying phase of the Sun and the solar system
The Sun is a relatively young star and is a part of the generation of stars called Population I. The members of Population I are generally young, hot and luminous. It is estimated that the Sun is halfway through its life, still will last for many more millions of years. According to scientists, in another 5 billion years, the hydrogen inside the star will exhaust and will become a hundred times brighter than at present. Thereafter, it will become red giant and swallow all near planets including the Earth. After another 100 million years, the Sun will shrink and become a white dwarf.
Dwarfs are small stars with low luminosity. Scientists call big stars giants and small stars dwarfs to describe the size. A white dwarf is a star that has used up its entire stock of hydrogen fuel and is dying. Slowly it too will fade and enter its final phase as a dim, cool theoretical object known as black dwarf. The Sun is currently in the yellow dwarf stage.