Argon –The Element and Its Applications
Argon is the third most abundant gas on Earth. Incandescent bulbs and Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFL) are two major light sources. Though, they apply two different methods for generation of light argon is employed in both bulbs.
Incandescent bulb and compact fluorescent lamps – Role of argon
Incandescent bulb produces light through thermal radiation. These types of bulbs contain a light thin metal filament made of tungsten connected on both sides by two wires. Emission of light occurs from this filament at high temperature through a process called Joule heating and the light is known as incandescence. Despite generating heat, in an incandescent bulb the filament keeps on burning for days and weeks without dying out or blackening the glass. This is due to the presence of the element argon. Argon is an inert gas and does not react with the filament even at high temperatures. If the glass is filled with another gas, it will react with the filament and the life span will be reduced substantially. The presence of the argon helps the filament to last long. However, it may be noted that the filament produces substantial heat during lighting process and it is essential to dissipate the heat to have long life time. The incandescent bulb has a special geometry and the shape of the spherical glass shell ensures dissipation of heat evenly in all directions.
The element argon is present in compact fluorescent lamps (CFL) also. CFL produce light by a method called fluorescence. The lamps contain mixture of argon and mercury vapors held at low pressure and this mixture when excited produces ultraviolet waves. These UV waves stimulate the fluorescent coating inside the bulb and produces visible light. In a CFL, UV radiation is produced along the length of the lamp, irrespective of the shape. Unlike in the incandescence bulbs, no heat energy is produced in CFLs and it offers lot of freedom in designing the shape of the lamp.
Application of argon in preservation
Argon is widely used in preservation of important historical documents. The element protects the documents from decay. Normally, oxygen present in atmosphere reacts with the paper and ink in the document and causes degradation of the document. If argon is pumped around the documents, it will displace the oxygen in the surroundings. As the gas is inert, it does not react with the paper or ink and the document can be preserved for long.
Application of argon in defense and industry
As mentioned above, argon helps generation of light in CFL without generation of heat. As no heat is generated, such lamps can be designed in various shapes. The freedom in design of lamps has transformed the decorative lighting industry. CFL lamps are available in different shapes and models. In defense, argon is used to cool the heads of heat seeking missiles. Due to this ability, argon is considered as a blessing in defense industry.
Discovery of argon
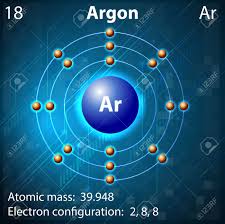
Lord Rayleigh, an English scientist and Sir William Ramsay, a Scottish chemist are credited with the discovery and naming of argon. The element is represented by the symbol Ar and has the atomic number 18. Hence, it occupies the eighteenth position in periodic table.
Though argon has specific roles in industry, it has no biological significance. Presence of large amounts of pure argon in enclosed areas is harmful and can lead to suffocation in people.
Which is the only element discovered first in space?
Why is phosphorus known as devil’s element?









Great Blog. The blog you have shared in the topic of "Argon Gase and its applications" is very useful and informative. Thanks for sharing this blog.