What are Optical Tweezers? Why is LASER in news?« Back to Questions List
|
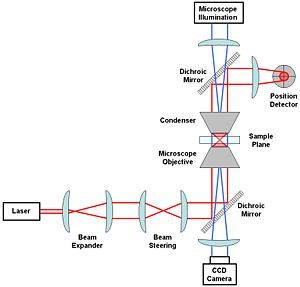
Optical Tweezers employ laser based technology that allows the force of laser beams to manipulate microorganisms like bacteria without causing damage to them. The Nobel Prize in Physics, 2018 awarded “for ground-breaking inventions in the field of laser physics” brought laser to the attention of the world once again. One half of the Nobel Prize was awarded to Arthur Ashkin and the other half jointly to Gérard Mourou and Donna Strickland. They are pioneers in the field of laser technology. LASER stands for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. This laser light is of one wavelength (one frequency) and of a single color. The highly directional characteristic of laser light can impact a force on the small area where it falls. This property was utilised by Arthur Ashkin in the development of Optical Tweezers in 1970s. The radiation pressure, pressure caused by the light, was thus put into usage. The application and breakthrough for the discovery came later when the Optical Tweezers began to be used for moving and manipulating complex but tiny objects like viruses and cells. At present optical Tweezers are widely used in the study of proteins, the inner life of cells and biological molecular motors. The present day technique being used to segregate healthy blood cells from infected ones is one of the applications of Optical Tweezers. Optical tweezers are now used for measuring distances also in the study of microorganisms. The second half of the Nobel Prize in Physics 2018 was awarded jointly to Gérard Mourou in France and Donna Strickland in Canada for their contributions for generating high-intensity, ultra-short optical pulses. Their laser based discovery, “chirped pulse amplification (CPA)” is employed in eye surgery. In this method, high intensity laser beams are used in corrective eye surgery without damaging tissues. The discovery is expected to contribute in solar cell technologies and faster electronics, in future. Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) is a technique employed for amplifying an ultrashort laser pulse up to the petawatt level. This is achieved by stretching out the laser pulse temporally and spectrally prior to amplification. This technique is now widely employed in almost all the high power lasers above 100 terawatts.
Dr Arthur Ashkin, at the age of 96 becomes the oldest Nobel laurate. Donna Strickland is the third woman in history to win the Physics Nobel prize. She follows Marie Curie (1903) and Maria Goeppert Mayer (1963). Why is LASER light used in surgeries?Directed Evolution (DE) and Nobel Prize for Chemistry 2018 |