How does water reach the leaves?« Back to Questions List
|
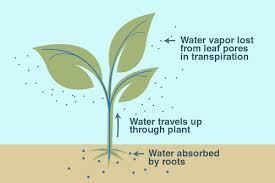
Have you ever imagined how does water reach the leaves of a coconut tree or teak tree or what forces them to travel all the way from the roots to the top? There could be hundreds of feet between the roots and the leaves of a tree. Great volumes of water make this trip at an amazing speed of 100 feet per hour. It all begins at the roots where water moves into root hairs by osmosis. Cells in the root hairs contain dissolved sugars and salts and the water moves into them from the surrounding soil to equalize the pressure. The increase in water pressure at the root hairs forces water upward, cell by cell, through the roots and trunk toward the top of the tree. This upward motion is still made stronger by one other force. While a tree grows, it passes tons of water into the atmosphere through its leaves by a process called transpiration. Only 1% of the water that is taken in is used during photosynthesis and remaining is lost by transpiration. This partial vacuum is quickly filled by the water being moved upward from the roots. The upward movement of water happens through the xylem tissue in the plant. Xylem transports water, dissolved minerals and other organic matters that reach them through roots. The fluid mixture of these ingredients is known as sap. In a tree, transportation occurs through the xylem present in the outermost tree ring. In plants, xylem is contained in the stem. The above described process can be split into three activities. They are diffusion, transpiration and capillary action. Water gets into the roots through the process called diffusion or osmosis. The salt concentration on the plant is higher compared to soil. In order to make the salt concentration equal, water travels from soil to plant. Though roots do not normally allow movement of salts from soil to plant, they do permit movement of water, minerals and small organic parts. The movement restriction happens because of the presence of a semi-permeable membrane. If the salt concentration inside the plant reduces, the membrane will allow salt also to enter into the root. Transpiration is the process for water movement throughout the plant. Plants lose water during respiration and photosynthesis. This happens through the leaf surface through stomata, or pores in the leaf surface. As the rate of evaporation increases, plant needs more water and the roots draw more water from the soil. More evaporation happens when heat and wind are more and transpiration is more during such weather conditions. Transpiration and evaporation rates are lower when relative humidity is lower. The activity of xylem depends on the chemical properties of water. Xylem has only small diameter. Water molecules have strong affinity to stick together. As more evaporation happens, leaves pull more water up through xylem. A water molecule on evaporation pulls next water molecule. This causes movement of water upward. The water molecule that sticks to the inside of xylem does not fall down. Hence only upward movement occurs and this process is called capillary action. The attraction among water molecules and that between water molecule and xylem make the capillary action easy. This process happens in trees. In plants, diffusion, transpiration and capillary action occur together. The pressure of the water that enters the root pushes the water upward through the xylem. Transpiration pulls the water molecule upwards. Simultaneous capillary action helps water molecule to overcome gravitational force. What helps the plant grow throughout their life? |